By using this website, you agree to our Privacy Policy
×
Perfect Sealing Solutions Using Rubber Extrusion
From the doors of your car to the high-pressure environments of aerospace technology, rubber seal extrusions provide critical protection and insulation across numerous applications. They offer flexible but entirely supportive components that ensure air, water, dust, and other contaminants are kept at bay, maintaining the integrity and performance of countless systems and structures used daily.
Rubber extrusion is a superior manufacturing method because it produces highly durable, cost-effective products with complex shapes. Unlike moulding, extrusion minimises material waste and is ideal for creating long, continuous items like hoses and pipes. The process allows various rubber types to be used and versatile solutions to be produced across industries. By tailoring dies to customer specifications, extrusion produces high-quality, long-lasting components that meet precise specifications. Rubber seals are the perfect fit for thousands of applications. This guide covers everything you need to know about rubber seal extrusions.
Introduction to Rubber Seal Extrusions
Rubber extrusion seals are continuous profiles of rubber material that are produced through the extrusion process. They are designed to create a tight seal between two surfaces, preventing the passage of air, water, dust, and other contaminants. Rubber seals primarily provide sealing, vibration damping, insulation, soundproofing, and protection from environmental factors.
Achieving a perfect seal requires careful attention to profile design. Key considerations include:
- Shape and size: The die determines the final profile, so precise design is crucial.
- Material selection: Choose rubber compounds based on application requirements for flexibility, strength, and resistance to temperature or chemicals.
- Wall thickness and tolerances: Uniform wall thickness and tight tolerances ensure consistent performance and fit.
- Surface finish: Smooth finishes help prevent leaks and improve durability.
- Customisation: Collaborating with experienced manufacturers enables the creation of profiles tailored to unique sealing challenges.
Addressing these factors during the design phase helps ensure long-lasting, effective sealing solutions.
Materials
Natural Rubber (NR)
Natural rubber is a non-synthetic rubber known for its excellent resilience, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand large deformations. One of its standout features is stress crystallisation (a phenomenon where the rubber strengthens when stretched under high stress), which enhances its tear resistance, making it an excellent material for dynamic seals. It is fully biodegradable and has good abrasion and cut resistance, making it suitable for general heavy-duty applications like engine mountings and earthquake isolators. However, its weakness lies in its vulnerability to ozone, UV, and petroleum-based oils, limiting its use in outdoor or chemically aggressive environments.
Polyisoprene (IR)
Polyisoprene is a synthetic alternative to natural rubber, replicating many of its properties but with slightly lower tensile strength and tear resistance. It's often preferred for applications where consistent purity is required, such as in medical devices and adhesives. Polyisoprene offers comparable elasticity and deformation properties but lacks the natural resilience of NR in extremely dynamic settings.
Shotblast Rubber
This variant of natural rubber is designed for high abrasion resistance and shock absorption. Shotblast rubber’s high tensile strength and elasticity make it a reliable option for heavy-duty sealing applications, such as chute linings and skirting rubber in industrial settings. Its excellent wear resistance allows it to endure continuous mechanical stress.
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
SBR is a widely used synthetic rubber, accounting for a significant portion of global rubber production. It offers high tensile strength, good abrasion resistance, and low-temperature flexibility, making it a cost-effective alternative to natural rubber for automotive seals, shoe soles, and gaskets. However, its susceptibility to ozone and UV exposure limits its outdoor applications. SBR is resistant to water and organic acids but not oils and fuels.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM)
EPDM is a highly versatile synthetic rubber with excellent weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor seal extrusions like roofing and automotive seals. It is also superiorly resistant to ozone, UV, and steam and can withstand high operating temperatures, making it suitable for long-life outdoor applications. However, its low compatibility with oils and fuels limits its usage in environments where petroleum exposure is common.
Butyl Rubber (IIR)
Butyl rubber is noted for its exceptionally low gas permeability, making it ideal for vacuum sealing and high-pressure applications. Its excellent resistance to weathering, ozone, and dilute acids makes it suitable for seals used in air and water applications, such as inner tubes and gaskets. However, it has poor compatibility with petroleum-based fluids and has low resilience, making it unsuitable for dynamic sealing applications.
Neoprene
Neoprene offers a balanced combination of oil, chemical, and weather resistance, making it one of the most versatile rubbers for seals. Its resilience, strength, and moderate cost make it ideal for V-belts, hoses, and weather stripping. Neoprene also has good heat resistance and flame retardancy, making it suitable for industrial and automotive seals. However, it performs poorly in extremely cold conditions and lacks the elasticity of NR or IR.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile is well-known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, making it the preferred material for seals in the automotive and aerospace industries. Its heat resistance further extends its applicability to high-temperature environments. However, NBR’s poor ozone and UV resistance limit its outdoor use. It is also sensitive to shrinkage in seals due to plasticiser loss, making careful material selection crucial.
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is ideal for high-temperature sealing applications, withstanding extremes from -80°C to +300°C. Due to its inert, non-toxic nature, it is widely used in the food, medical, and pharmaceutical industries. Its flexibility at low temperatures and excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance make it suitable for outdoor sealing applications. However, silicone is less durable in terms of abrasion and has a high production cost, limiting its use to specialised applications.
Fluorocarbon Rubber (FKM)
Fluorocarbon rubber, commonly known as Viton, is highly resistant to heat, chemicals, and fuels, making it ideal for seals in high-temperature industrial environments. Its ability to maintain performance in continuous service at temperatures up to 300°C makes it a premium choice for extreme applications, such as gaskets and seals in fuel systems. However, its poor low-temperature flexibility and high cost make it less suitable for standard sealing requirements.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
TPE combines the elasticity of rubber with the recyclability of plastics, making it an environmentally friendly option for seal extrusions. Due to its excellent vibration-damping and shock-absorbing properties, it is commonly used in automotive and construction applications. However, its relatively high cost and limited temperature range restrict its use to specific applications.
Comparing Material Properties
Rubber Type | Durability | Elasticity | Chemical Resistance | Cost |
Natural Rubber (NR) | Excellent abrasion and tear resistance but poor UV and ozone resistance | Very high elasticity | Limited: resistant to water, acids, and alkalis; not suitable for oils | Moderate: lower-cost natural option |
Styrene Butadiene (SBR) | Good abrasion resistance, poor weather resistance | Good elasticity, less than NR | Good for water and chemicals but poor for oils and fuels | Low-cost alternative to NR |
EPDM | Excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance | High elasticity | Excellent resistance to chemicals like acids and alkalis | Moderate to high, depending on the compound |
Butyl Rubber (IIR) | Excellent weather resistance, low permeability to gases | Low resilience | Suitable for dilute acids/alkalis, not suited for oils or petroleum | Moderate |
Neoprene | Good overall durability, including weather and heat resistance | Moderate elasticity | Moderate oil and chemical resistance, good against alcohols and oils | Moderate |
Nitrile (NBR) | Excellent oil and fuel resistance, good heat resistance | Moderate elasticity | Excellent for oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons; poor ozone/UV resistance | Moderate |
Silicone | Excellent temperature resistance, lower abrasion resistance | Very high elasticity across a wide temperature range | Good chemical resistance, but poor in oils and fuels | High |
Fluorocarbon (Viton) | Excellent high-temperature resistance and durability | Low elasticity | Excellent resistance to chemicals, oils, fuels | Very high |
Polyisoprene (IR) | Comparable to natural rubber with slightly lower durability | High elasticity | Limited chemical resistance, similar to NR | Moderate |
Advanced Materials and Nanotechnology
Recent advancements in rubber technology include the addition of nanomaterials, such as silica nanoparticles, nanoclays, and carbon nanotubes, to rubber compounds. These nanofillers can significantly increase mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, flame retardancy, and even electrical or thermal conductivity. For example, nanoclays improve both mechanical properties and flame resistance, while carbon nanotubes boost tensile strength and fatigue resistance. These innovations are especially valuable for demanding sealing applications in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
Sustainability in Rubber Production
The sustainability of rubber varies significantly across types. Natural rubber is the most sustainable due to its biodegradability and renewable source, though concerns over deforestation and ethical harvesting remain. EPDM and neoprene are synthetic rubbers with good durability and recyclability, but they rely on fossil fuels, making them less eco-friendly. Silicone is energy-intensive to produce yet long-lasting and recyclable, while nitrile offers strong chemical resistance but has limited sustainability, largely depending on petrochemicals. The push towards greener practices in the rubber industry highlights the importance of finding eco-friendly alternatives and improving recycling methods.
The Extrusion Process for Rubber Seals
The extrusion process involves forcing rubber through a die to create continuous lengths of a specific cross-sectional profile.
Material preparation: the rubber compound is mixed and prepared.
Extrusion: the compound is fed into an extruder, heated, and forced through a die to form the desired shape.
Curing/vulcanisation: the extruded profile is cured to enhance its strength and elasticity. This is done through heat or chemical processes.
Cutting and finishing: the extruded rubber is cut to length and finished as required.
Quality Control in Rubber Extrusion
Quality control in rubber extrusion ensures that rubber seals meet strict performance standards. It starts with raw material inspection, where the rubber and additives are tested for purity and consistency to avoid defects later in the process. Regular supplier audits help maintain consistent material quality. During extrusion, process control is critical; careful monitoring of temperature and pressure settings prevents issues like cracking or blistering.
In-process testing includes dimensional checks using precision tools to verify the extruded profiles meet required tolerances, while visual inspections ensure surfaces are free from defects. Physical property testing assesses tensile strength, hardness, and resilience, ensuring the product's durability under its intended application.
Final product testing evaluates the rubber’s mechanical and chemical properties, including resistance to wear, chemicals, and environmental factors like UV and ozone. These tests ensure the seals will perform reliably in challenging conditions. Detailed documentation of all tests provides traceability, supports audits, and helps refine production processes. This comprehensive approach ensures compliance with industry standards, such as ISO 9001, and continuous quality improvement, ultimately delivering reliable seals for various industries. Find out more about quality standards further on in this guide.
Defects and Troubleshooting in Rubber Seal Extrusions
Even with advanced manufacturing processes, rubber seal extrusions can sometimes experience several defects that impact performance and appearance. These include:
Surface imperfections: Scratches, bumps, and pits can occur during extrusion, potentially leading to leaks or reduced sealing capability.
Dimensional inaccuracies: Variations in raw materials or die design can result in profiles that do not meet specified dimensions.
Poor wall uniformity: Inconsistent wall thickness creates weak spots and can affect fit and durability.
Incomplete curing: Insufficient curing leaves the material soft or sticky, compromising functionality.
Contamination: Introduction of foreign materials, such as dust or debris, can reduce adhesion and cause premature wear.
Working with experienced manufacturers and implementing robust quality control measures is essential to minimise these issues and ensure reliable sealing solutions.
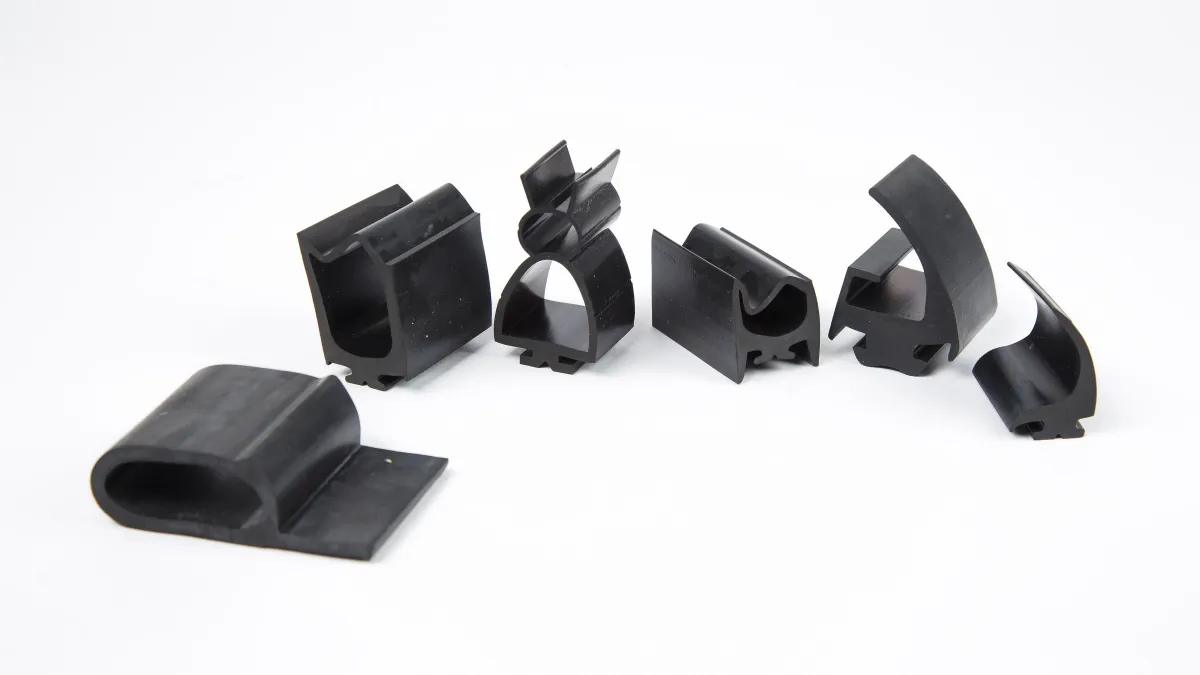
Profiles and Shapes
Rubber seal extrusions come in various profiles and shapes to suit different applications. Here’s a list of types of rubber seals:
U-Channels
D-Seals
P-Seals
T-Seals
E-Seals
Lip Seals
Bulb Seals
Custom Profiles
Seal Type | Uses | Reasons for Choosing | Real-Life Example |
U-Channels | Edging, sealing, and protective covers | Flexible, easy to install, good for edge protection | Used in car door edges to prevent damage and seal gaps |
D-Seals | Weatherstripping, door and window seals | Good compression, excellent sealing properties | Used in refrigerator doors to maintain a tight seal |
P-Seals | Sealing and cushioning applications | Effective at sealing, provides cushioning | Used in aircraft doors for effective sealing and cushioning |
T-Seals | Dynamic sealing applications | High wear resistance, low friction | Used in hydraulic cylinder rods to prevent fluid leakage |
E-Seals | Edge seals, weatherstripping | Good flexibility, durable | Used in industrial machinery to seal panel edges |
Lip Seals | Rotating shafts, hydraulic cylinders | Excellent sealing for rotating parts, high-pressure resistance | Used in automotive engines to seal crankshafts |
Bulb Seals | Doors, hatches, and enclosures | Provides a tight seal and excellent compression properties | Used in marine hatch covers to prevent water ingress |
Custom Profiles | Specialised sealing, insulation, and protection needs | Tailored to specific applications, highly customisable | Used in medical devices to provide specialised sealing |
Choosing the Right Seal for the Application
When selecting the right rubber extruded seal, consider both the material and profile. Material selection depends on environmental factors such as temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure. EPDM is ideal for outdoor applications due to its resistance to UV and ozone, while Nitrile is excellent for sealing against oils and fuels. Silicone or Fluorocarbon (FKM) may be necessary if high temperatures are a concern.
Choosing the seal profile depends on the specific function. U-channels are generally used for edge protection in car doors, offering flexibility and easy installation. D-seals are widely used in weatherstripping, like in refrigerator doors, where excellent compression and sealing are needed. For dynamic sealing applications, T-seals are ideal due to their low friction and high wear resistance—commonly used in hydraulic systems. P-seals offer both sealing and cushioning, making them a go-to for aircraft doors. Lip seals are crucial in rotating shafts and high-pressure environments, while bulb seals provide a watertight seal for doors and hatches in marine environments.
To ensure the correct profile and material, evaluate factors like compression set, hardness, and dimensional tolerances. Collaborate with a high-quality manufacturer to customise the seal for your exact needs to deliver optimal performance.
Custom rubber seals are designed when standard options fail to meet specific requirements. They offer precise, durable sealing solutions tailored to industries like automotive or construction. Manufacturers use existing samples or technical digital reconstructions to extrude seals from materials such as EPDM, Neoprene, or Silicone, ensuring chemical and environmental compatibility, with flexible production runs and rapid prototyping available.
Standards and Specifications
Rubber seal extrusions often need to meet specific standards depending on the industry and application. These include:
UK-Specific Standards:
- BSI (British Standards Institution): The UK’s national standards body which provides standards for various rubber products.
BS 2751: specification for acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR) used in oil and fuel resistance applications.
BS 4443: methods of test for assessing the effects of liquids on vulcanised rubber.
BS 903: general physical testing methods for rubber.
BS EN 681-1: concerns elastomeric seals and material requirements for pipe joint seals used in water and drainage applications.
International and General Standards:
ASTM Standards: various ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards for rubber properties. Examples include ASTM D2000 for rubber materials and ASTM D1149 for rubber deterioration.
ISO Standards: international standards for rubber materials and products. Examples include ISO 3302 for tolerances and ISO 37 for tensile testing.
Industry-Specific Standards:
- OEM Specifications: original equipment manufacturer specifications for automotive and aerospace applications ensure that the rubber seal extrusions meet the manufacturers' precise requirements.
Automotive: OEM specifications from companies like Ford and Jaguar Land Rover often outline specific requirements for vehicle rubber seals.
Aerospace: OEM specifications from companies like Rolls-Royce and BAE Systems for rubber seals used in aircraft and aerospace components.
How are rubber seals tested for quality?
Testing the quality of rubber seals involves several key methods to ensure they meet performance standards. One common test is for hardness, using either Shore A or IRHD (International Rubber Hardness Degrees) to measure resistance to indentation. Tensile strength is also assessed, determining how much force the rubber can withstand before breaking, which is crucial for seals in dynamic applications. Compression set testing evaluates the material's ability to return to its original shape after being compressed, which ensures the seal maintains its integrity over time.
In addition to these physical tests, fluid resistance is examined through soak testing, where seals are exposed to various chemicals to ensure they don't degrade or swell. For more in-depth analysis, Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Gas Chromatography can be used to identify the chemical makeup of the rubber and any potential weaknesses in composition.
These tests are particularly important in industries with high safety demands, such as automotive or aerospace, where seal failure could lead to significant issues. Comprehensive testing helps ensure long-term reliability, and working with trusted suppliers guarantees that the rubber meets both industry standards and specific application requirements.
Applications in Various Industries
Rubber seal extrusions are vital components that hold the integrity of millions of different items together. In the automotive sector, these seals are essential for door seals, window seals, trunk seals, and weatherstripping. They ensure that vehicles remain airtight and protected from external elements, reduce noise, and improve energy efficiency.
In construction, rubber seal extrusions are important in effectively sealing windows and doors, preventing water ingress and air leaks in buildings. They are also used in expansion joints to accommodate structural movements and ensure the longevity of structures.
The marine industry relies heavily on rubber seal extrusions for hatch seals, porthole seals, and deck seals, where they protect against water ingress and harsh marine environments, enhancing the safety and durability of marine vessels. They’re also critical in the defence sector for similar purposes.
In the aerospace industry, rubber seals are indispensable for door, window, and panel seals. They maintain cabin pressure and protect against environmental factors at high altitudes.
Industrial applications of rubber seal extrusions include gaskets, vibration dampers, and protective barriers. These seals are used in machinery and equipment to prevent leaks, reduce vibrations, and protect sensitive components from contamination and damage.
Niche Applications
Solar Panel Seals: In renewable energy, rubber extruded seals protect solar panels from harsh environmental conditions such as UV exposure, rain, and extreme temperatures. EPDM rubber seals are commonly used in these applications, supporting the longevity and efficiency of solar power systems.
Aerospace Door Seals: Aerospace applications require highly specialised seals for cabin doors, cargo areas, and windows. Silicone rubber seals are often chosen for their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and maintain flexibility in high-altitude conditions to protect airtight cabins and prevent temperature and pressure fluctuations inside aircraft.
Pharmaceutical Equipment Seals: Rubber extruded seals are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment, where hygiene and contamination prevention are critical. ISO-certified silicone rubber seals are frequently used in sterilisation chambers, pumps, and fluid transfer systems due to their non-reactivity, flexibility, and ability to withstand frequent cleaning and sterilisation cycles.
Find out about different rubber extrusion seals in detail:
Benefits of Using Rubber Seal Extrusions
One of the primary advantages of rubber seal extrusions is their flexibility and durability. Rubber seals are inherently flexible, allowing them to withstand repeated deformation while maintaining their sealing properties. This resilience means they stand up to being bent and flexed, whether that’s installing them in awkward spaces or repeated movement over time as part of their application.
Another significant benefit of rubber seal extrusions is their weather resistance. Many rubber materials, such as EPDM and silicone, are highly resistant to environmental factors, including UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures. EPDM can withstand -50°C to +120°/150°C, and silicone can withstand -60°C up to +230°C. This makes them suitable for indoor and outdoor applications where exposure to harsh conditions is common.
Chemical resistance is also a key feature of certain rubber types, such as neoprene and nitrile. Nitrile can resist a range of acids, alkalis, and solvents, and neoprene can resist solvents, oils and petroleum-based fuel, among other substances. These materials are perfect for use in automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications where exposure to such chemicals is frequent.
Rubber seal extrusions significantly reduce lifecycle costs by minimising the need for frequent replacements and maintenance, thanks to their long-lasting durability and resistance to environmental factors like UV, ozone, and chemicals. These seals also improve energy efficiency by preventing leaks in systems like HVAC or hydraulic equipment.
Compared to alternatives like plastic or foam, rubber offers superior flexibility and compression set resistance, maintaining its shape under constant pressure and movement. While plastic can crack, and foam lacks durability, rubber's wear resistance makes it ideal for dynamic environments such as automotive and industrial applications, leading to better long-term savings.
Rubber seal extrusions have the significant advantage of being customisable. With custom profiles and materials, they can be tailored to meet specific application requirements. This ability to customise ensures that the seals provide the optimal performance needed for unique and demanding applications, enhancing their functionality and efficiency.
Customisation Options for Seal Extrusions
Custom-Made Rubber Seal Extrusions are tailored to meet specific requirements. The process starts with a detailed application analysis to determine the precise dimensions, shape, and material properties needed. A custom die is then created to produce the exact profile required. Custom seals are ideal for unique or highly specialised applications where standard seals would not suffice. They offer a perfect fit, enhanced performance, and specific properties like unique chemical resistance, flexibility, or hardness tailored to the operating environment. For example, a custom seal might be designed to fit an irregularly shaped groove in an aerospace component or to withstand extreme temperatures in a specialised industrial machine.
Standard Rubber Seal Extrusions, on the other hand, are pre-manufactured to common shapes and sizes, such as U-channels, D-seals, and P-seals. These can be mass-produced using standard dies and are readily available. They are suitable for general-purpose applications where precise specifications are not as critical or where the application is designed to meet generalised specifications. Standard seals offer cost-effectiveness and quicker availability compared to custom-made seals. They are often used in more routine applications, such as standard automotive door seals or basic window weatherstripping in construction.
Innovations and Future Trends in Rubber Sealing Technology
Smart Seals with Embedded Sensors
One noted innovation in rubber sealing technology is the development of smart seals with embedded sensors. The seals use advanced sensor technology to monitor real-time parameters such as pressure, temperature, and wear. The embedded sensors provide continuous feedback to support predictive maintenance and early detection of potential failures. By integrating these smart seals into systems, manufacturers can reduce downtime, optimise maintenance schedules, and improve safety and efficiency.
Freudenberg Sealing Technologies is a key player in this field. They have developed intelligent seals capable of monitoring their own state of wear and handling sensor applications. Their smart seals incorporate built-in functionality to act as sensors, providing data about their performance and safety, which helps prevent mechanical failures and unplanned downtime. One notable development is their intelligent rod seal, which forms a capacitor to measure wear and predict the seal's remaining service life.
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Materials
Another emerging trend looks towards eco-friendly and sustainable materials in rubber sealing. With growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures, the industry is developing seals made from biodegradable or recyclable rubber compounds. Innovations include the use of natural rubber sourced from sustainable plantations and the development of synthetic rubbers with reduced environmental impact. The core focus is on improving the life cycle of seals by enhancing their durability and resistance to degradation to reduce the frequency of replacements and waste production. These sustainable seals are increasingly being adopted in automotive, construction, and consumer goods industries, aligning with global sustainability and environmental conservation efforts.
Our blog uncovers everything you need to know about rubber extrusion products, from processes to custom designs to what we recommend for which applications. Take a look at our rubber extrusion blog or browse all the products we make to order.




news
Continue reading
Speak to One of Our Experts
Contact UsLEARN
INDUSTRIES
PRODUCTS
BRANDS
GET IN TOUCH


- © 2025 Nufox. All rights reserved |
- Terms & Conditions |
- Privacy Policy |
- Download ISO Certificate | Web Design MadeByShape