By using this website, you agree to our Privacy Policy
×
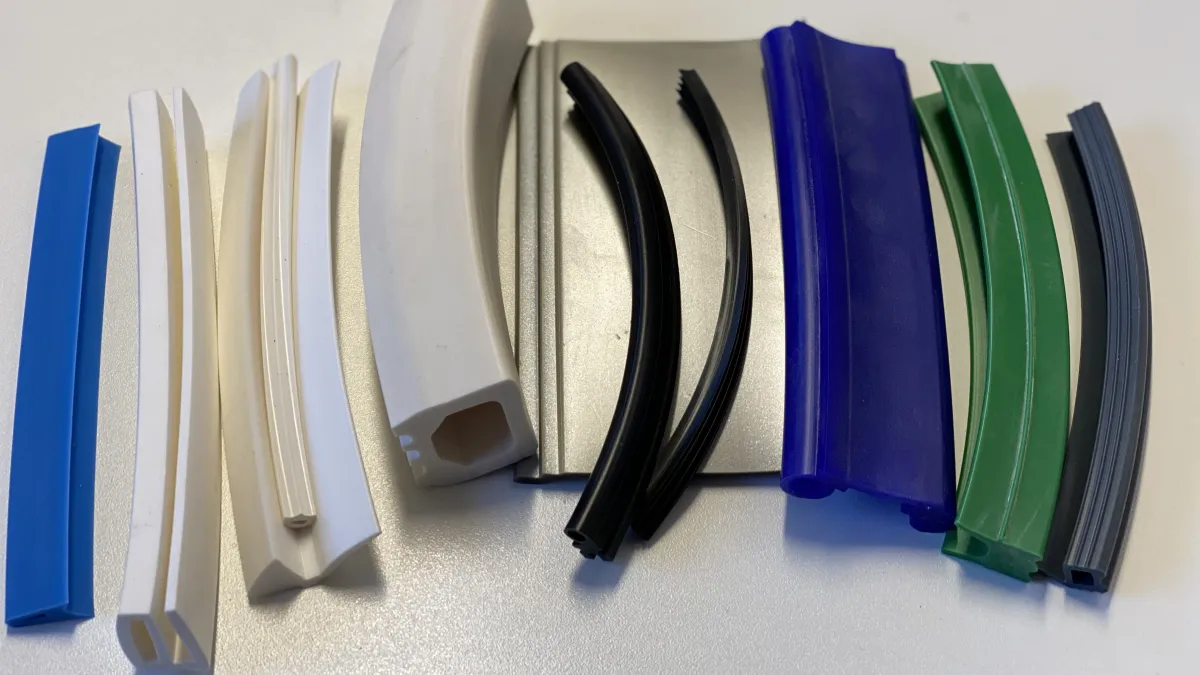
The Versatility of Silicone Rubber Extrusions

Silicone rubber bears properties that enable its use in extreme conditions, through exposure to a wide range of chemicals, and even resistance to UV light, without degrading in quality. It is a highly reliable material and can be used in rubber extrusion to produce products that help us advance technology, engineering, and innovation in many industries. Here’s everything you need to know about silicone rubber extrusion.
Introduction to Silicone Rubber Extrusions
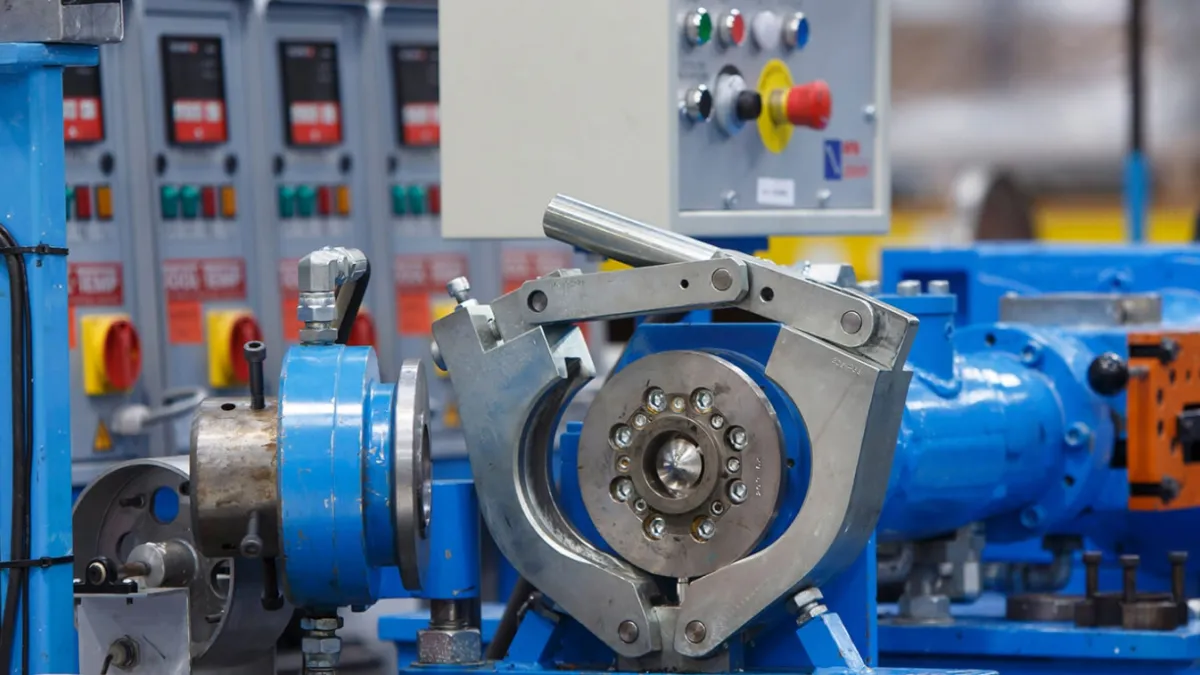
Silicone rubber extrusion is the process of shaping silicone rubber into a specific, continuous, uniform shape determined by a cross-sectional hollow known as a profile. The process involves feeding rubber strips or pellets into a machine that gradually heats and softens the rubber and kneads it by shear force until it can be pressed through a uniquely shaped hole (the profile).
The physical process of rubber extrusion is generally the same, no matter the type of rubber. You can find out how it works in our guide, Understanding Rubber Extrusions: A Comprehensive Guide. This article focuses on silicone rubber, how its extruded form is different from raw, natural rubber, and why or when we use silicone rubber over other rubber compounds.
First, let’s examine silicone in more detail.
About Silicone Rubber
Created in 1943, silicone is now widely manufactured worldwide. It is a high-performance elastomer, a material composed of chain-like polymers that can recover its shape when stretched.Silicone rubber was first developed in 1943 by General Electric and Corning Glass Works as it sought a heat-resistant insulating material for motors and generators. Their breakthrough innovation provided a material that could withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemical exposure. This discovery paved the way for silicone's widespread use in automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics industries. Over the years, silicone's unique combination of flexibility, durability, and resistance to heat, chemicals, and weather conditions has led to its application in various products, from medical devices to household items.
How is silicone made?
Unlike natural rubber, which is derived from the latex produced by rubber trees and composed of polyisoprene, which provides high elasticity and tensile strength, silicone rubber is a synthetic polymer based on silicon that has excellent heat and chemical-resistance properties.
The key ingredients used in the production of silicone rubber are silica quartz, methyl chloride, curing agents, and some other additives. Silicone rubber is created from an inorganic silicon-oxygen (Si-O) backbone with organic functional groups attached. This Si-O bond gives silicone its high-temperature resistance and flexibility over a wide range of temperatures. The process begins with silica extracted from quartz sand, heated to 1800°C to extract silicon atoms. These are combined with methyl chloride and distilled to create silicone polymers.
The silicone polymer is then mixed with reinforcing fillers and processing aids to form a stiff gum. This gum is crosslinked at elevated temperatures using either peroxides or polyaddition curing, turning it into a solid elastomeric material.
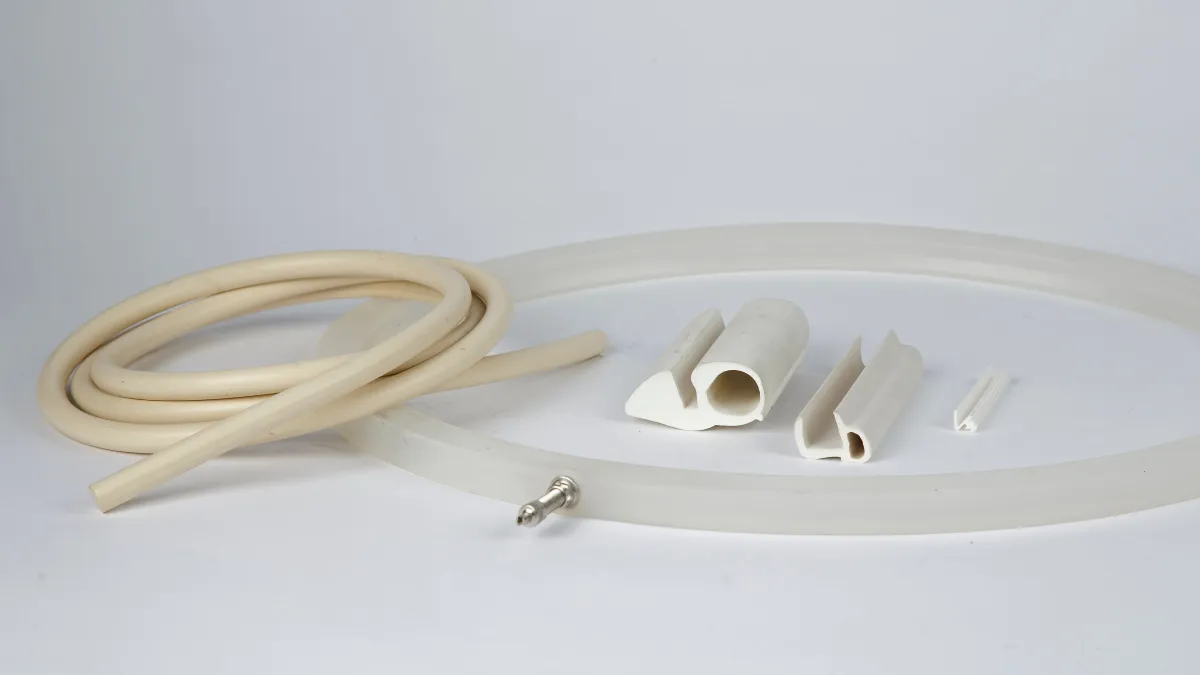
Because of this, silicone rubber extrusions can be customised to meet specific industry needs, giving flexibility and adaptability across a wide range of applications and providing superior performance in demanding environments where niche, bespoke-made products must be relied on. Silicone rubber extrusions can be tailored to precise requirements, including a wide range of durometers (hardness), colors, surface finishes, and even complex multi-lumen or co-extruded profiles.
The Extrusion Process
Silicone rubber extrusion involves forcing uncured silicone material through a heated extruder and a die, which shapes the silicone into a continuous profile based on the die's cross-sectional design. The extruded material is then cured through heat or another curing method to set its shape and ensure durability. This process is ideal for creating seals, gaskets, and tubing with consistent, customised dimensions for various applications. Injecting gases like nitrogen into the silicone during extrusion creates a closed-cell sponge, ideal for watertight seals.
‘Silicone’ not ‘Silicon’
Sometimes there’s a confusion between ‘silicone’ and ‘silicon’, so let’s clear that up. Although the names are almost identical, they’re actually different materials. Silicon is a natural chemical element (Si) found in sand and used in electronics due to its semiconducting properties. Silicone, on the other hand, is a synthetic polymer made from silicon, oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. Silicone contains silicon, but they’re not the same thing.
Applications in Various Industries
Silicone’s specific composition and properties make it a better choice for certain products. Thanks to advanced manufacturing techniques, silicone extrusions can be produced with complex geometries and tight tolerances, meeting the highest precision standards required for specialised applications.
Here’s a guide to where silicone rubber extrusions are commonly used.
Automotive Industry
Applications: Door seals, hoses, rubber gaskets, vibration-dampening components
With excellent sealing capabilities
Extreme temperature resistance
Durability under harsh conditions
Long-lasting performance
Medical and Healthcare
Applications: Medical tubing, seals, gaskets, surgical instruments, and healthcare equipment
Biocompatibility
Sterility (and ability to withstand repeated sterility)
Non-toxicity
Non-reactivity
Electronics
Applications: Insulation for cables and wires, gaskets for electronic enclosures, seals for connectors
Electric insulation properties
Durability
Resistance to heat and electrical interference
Construction and Architecture
Applications: Window and door seals, expansion joints, weatherproofing solutions
UV stability
Weather resistance
Flexibility
Reliable performance in sealing
Food and Beverage Industry
Applications: Gaskets, seals, tubing for food processing and packaging equipment
Compliance with food-grade standards
High-temperature resistance
Maintains integrity in contact with food
Silicone extrusions are used in food preparation in baking mats, food storage seals, conveyor belts, and non-stick cooking utensils. They are prized for their heat resistance, durability, and ability to maintain hygiene by resisting bacterial growth. Silicone’s non-porous nature prevents bacterial buildup, such as E. coli and MRSA, which is crucial for applications in food and medical industries.
Silicone rubber extrusions comply with food safety standards, too. Food-grade silicone is an FDA-approved, non-toxic and chemically inert material. It does not react with food or beverages and won't leach harmful chemicals even when exposed to high or low temperatures. This makes it great for manufacturing kitchen tools like spatulas, baking mats, and moulds. For extra safety precautions, food-grade silicone can also contain metal particles to identify broken parts easily during food processing via metal detection.
Aerospace and Defense
Applications: Silicone rubber extrusions in aerospace are ideal for aircraft seals, gaskets, and vibration-dampening components, supporting their function in extreme conditions at high altitudes and high speeds
Lightweight
Durable
Can withstand extreme temperatures and environmental conditions.
HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
Applications: Gaskets and seals in air handling units, ductwork, HVAC enclosures, and refrigeration systems
Sealing against air leakage
Temperature resistance
Flexibility
Industrial and Manufacturing
Applications: Conveyor belts, seals in food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and other industrial equipment
Temperature resistance
Chemical resistance
Resistance to mechanical wear
Efficient and reliable
Energy and Power
Applications: Sealing and insulating applications in power generation equipment, transformers, switchgear, and electrical enclosures
Sealing against environmental factors
Electrical insulation properties
Marine and Offshore
Applications: Seals and protection for boat and shipbuilding, offshore platforms, and marine equipment
Resistance to saltwater
Resistance to UV radiation
Can withstand extreme temperatures
Reliable performance and longevity
Unexpected Industries Using Silicone Extrusions
Beauty: Silicone is commonly used in beauty tools such as makeup applicators, facial cleansing brushes, and skin massagers due to its hypoallergenic properties and soft texture. It provides a skin-friendly material that’s easy to clean.
Agriculture: Silicone extrusions are widely used in agricultural applications due to their durability and resistance to harsh weather, chemicals, and UV exposure. They are commonly used for seals in greenhouse windows, tubing for irrigation systems, and livestock identification devices. Silicone’s chemical stability also makes it resistant to degradation from fertilisers and pesticides, securing long-term performance in challenging environments.
Beyond traditional sealing and insulation, silicone rubber extrusions are increasingly engineered with advanced functionalities. These include antimicrobial additives for use in healthcare, food processing, and public spaces, which help inhibit bacterial growth on surfaces. As demand for multifunctional components grows, smart silicone extrusions are set to play a key role in next-generation products.
Advantages of Silicone Rubber Extrusions
Silicone rubber bears several key advantages, making it a better choice than other materials. But it depends on what you’re looking for. Here are the benefits of silicone rubber in extrusion.
The most prominent advantage of silicone rubber is its temperature resistance. Thanks to its molecular structure, it remains stable and flexible, which means it can withstand temperatures as low as -60°C up to +230°C without degrading. The same is not the case with natural rubber, which becomes brittle and breaks down. Silicone rubber is a great choice for household objects like oven mitts and specialist items like medical devices that need to be autoclaved. The fact that silicone rubber remains flexible even at very low temperatures means it can be used to create products that need to be malleable in extremely low-temperature conditions.
Additionally, silicone rubber offers high tensile strength, making it resistant to abrasion and fatigue, which makes it suitable for demanding industrial applications. Silicone rubber extrusions' high tensile strength is particularly valuable in applications where the material is subject to heavy use, pressure, and environmental stress. For example, in the automotive industry, silicone rubber is used for engine gaskets and seals. These components must withstand extreme temperatures and constant movement without losing their integrity. The high tensile strength helps the silicone resist abrasion and fatigue, ensuring the seals maintain a tight, leak-proof fit even under prolonged stress and harsh conditions.
Strong molecular bonds in silicone rubber's structure make it a highly durable material. Silicone rubber's high durability stems from its silicon-oxygen backbone, which forms strong, stable bonds that resist heat, UV light, and chemicals. In contrast, natural rubber's carbon-based structure is more susceptible to degradation, making silicone rubber superior for more demanding applications and environments.
Silicones are generally chemically inert and are only attacked by some materials, including concentrated sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, and high-pressure steam over long-term exposure. Silicone can absorb materials with similar solubility parameters (a calling card of elastomers), causing slight swelling and softening. This swelling can be advantageous in some applications, like gaskets forming tighter seals when exposed to certain solvents. The changes are mainly physical; silicone rubber returns to its original properties once the solvent evaporates. Meanwhile, silicone’s chemical resistance makes it ideal for products that need to withstand chemical exposure, like medical tubing and seals.
There’s a long list of other advantages to using silicone rubber for extrusion projects.
Due to its high dielectric strength, silicone rubber is an excellent electrical insulator, which is beneficial for applications in the electrical and electronics industries.
Thanks to their chemically inert and stable composition, medical and food-grade silicone rubbers are biocompatible, non-toxic, and can be sterilised. This makes them suitable for medical devices, implants, and food-handling equipment.
Due to their resilient elastomeric network, silicone rubber extrusions exhibit low compression set, meaning they can return to their original shape after compression. This is vital for sealing applications.
For optimal performance in specialised environments, silicone rubber extrusions can be customised to suit exact specifications, from size and shape to material properties.
Certain silicone rubber formulations are inherently flame-retardant due to the presence of flame-retardant additives, providing an added level of safety in applications where fire resistance is crucial.
Because of its viscoelastic properties, silicone rubber can be easily extruded into complex shapes and designs, making the manufacturing process efficient and versatile.
Silicone rubber does not stain materials it comes into contact with and is generally non-toxic due to its inert nature, making it suitable for sensitive applications.
Silicone rubber is a reusable plastic polymer and, thus, an environmentally friendly alternative to single-use plastics, particularly in industries such as food and consumer products.
Designed for high tear strength, inflatable silicone rubber is used in industries requiring pneumatic seals and airtight sealing.
Silicone extrusions can be pigmented to match any colour, offering tailored solutions for brand consistency, particularly in food and drink manufacturing.
Silicone extrusions can be produced in small quantities, reducing costs for businesses with low-volume orders or specialised projects.
Despite its many advantages, silicone rubber has some limitations, including poor resistance to oils and fuels, weak adhesion to certain materials, and lower tear strength than other elastomers like EPDM. Scroll down for a more in-depth comparison of silicone to other types of rubber.
Differences Between Silicone and Other Rubber Extrusions
Thanks to its unique molecular composition, silicone rubber offers superior temperature resistance, chemical stability, and environmental durability over natural rubber. Because of this, it is ideal for extrusions intended for use in harsh conditions and extreme environments.
Temperature Resistance | |
Silicone Rubber Can withstand a broad temperature range from -50°C to 305°C making its performance reliable in extreme temperature conditions. | Natural Rubber Peforms well in a more narrow temperature range, normally up to 80°C and begins to degrade at higher temperatures. |
Environmental and Chemical Resistance | |
Silicone Rubber Highly resistant to UV radiation, ozone, oxygen and a range of chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor use and harsh conditions. | Natural Rubber More suited to indoor use and applications requiring high elasticity due to UV susceptibility. |
Mechanical Properties | |
Silicone Rubber Good flexibility, low toxicity, high bio-compatibility, and non-stick and non-adhesive properties. It is ideal for electrical insulation. | Natural Rubber Superior tensile strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance make natural rubber well-suited to the production of tyres, hoses, and seals. |
Silicone Grades
Silicone rubber comes in various grades tailored to specific applications, such as high-temperature silicone for automotive and aerospace components and fluorosilicone for military use. Electrically conductive silicone is ideal for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, while medical-grade silicone is used for biocompatible implants and tubing.
Here’s a detailed overview of key silicone grades:
General Purpose Silicone Rubber: This versatile grade operates across a wide temperature range, from low to very high. It’s commonly used for extrusion profiles, moulds, tubing, and sealants in food, pharmaceutical, and automotive industries. It is naturally translucent, easily pigmented, and boasts excellent tensile strength and chemical resistance.
Weather-Resistant Silicone Rubber: This grade excels in harsh outdoor conditions, resisting UV light, ozone, oxygen, and environmental stress. Unlike other rubbers that degrade over time, weather-resistant silicone remains intact, making it ideal for applications like seals and gaskets exposed to the elements.
Heat Stabilised Silicone Rubber: With additives allowing it to operate up to 260°C, this grade is available from 30° Shore A to 80° Shore A. Its elasticity ensures that it stretches under heat and returns to its original form when cooled, making it perfect for high-temperature industrial applications such as engine gaskets.
High-Temperature Silicone Rubber: This grade withstands even higher temperatures, up to 300°C, and is used in applications requiring extreme heat resistance, such as in industrial ovens or aerospace components. Available in a range of hardness from 40° to 80° Shore A, it is a preferred choice where heat stability is critical.
High Tear Strength Silicone: FDA-approved and available in hardness from 50° to 70° Shore A, this grade offers superior tear strength and elongation compared to general-purpose silicone. It’s used in applications requiring extra durability, such as mouldings, gaskets, and medical devices.
Platinum-Cured Silicone: This type undergoes a platinum-catalysed crosslinking process, providing low shrinkage and longer shelf life. Known for its high tear strength and optical translucency, platinum-cured silicone is often used in medical and food-safe applications due to its purity and stability.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR): A low-viscosity, high-purity elastomer, LSR is ideal for healthcare products and mechanical moulds. It retains its properties over a wide temperature range, with excellent heat and cold resistance. LSR is widely used in applications requiring precision, such as medical devices and consumer goods.
Steam Resistant Silicone Rubber: Specifically developed to withstand high-pressure steam environments, this grade can operate between -60°C to +260°C, making it ideal for industrial applications where steam exposure is a factor, such as in food processing equipment.
Inflatable Grade Silicone: Designed for pneumatic seals, this high tear strength, FDA-approved silicone is used in applications like inflatable seals for containment or pressure systems, offering reliable performance in demanding environments.
Fluorosilicone Rubber: This silicone variant is highly resistant to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it a popular material for aerospace and automotive fuel systems, where exposure to harsh chemicals is frequent.
Electrically Conductive Silicone: Specifically formulated to allow for electrical conductivity, this grade is used in electronic components, shielding applications, and EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) protection, offering a combination of flexibility and conductivity.
Medical-Grade Silicone: Known for its biocompatibility, medical-grade silicone is widely used in healthcare and medical device manufacturing, such as implants and tubing, due to its purity, non-toxicity, and durability under sterilisation conditions
Choosing the Right Type of Silicone for An Application
When selecting the right type of silicone rubber for an application, we need to consider the following factors to ensure optimal performance:
Temperature Range: Assessing whether the silicone needs to withstand extreme heat or cold. High-temperature silicone rubber can resist temperatures up to 300°C, while other grades, such as general-purpose silicone, may offer lower heat resistance.
Chemical Resistance: If the application involves exposure to chemicals, such as oils, fuels, or cleaning agents, fluorosilicone rubber offers superior chemical stability. Standard silicone's chemical resistance may suffice for environments exposed to fertilisers or pesticides.
Hardness (Shore A): Selecting the appropriate hardness level depending on the required flexibility and durability. Applications needing more durability may require higher Shore A values (e.g., 80), while softer materials (e.g., 30 Shore A) provide greater flexibility.
Environmental Exposure: For outdoor applications, such as in construction or agriculture, ensure the silicone offers UV, ozone, and weather resistance to prevent degradation. Weather-resistant silicone and EPDM are ideal for prolonged environmental exposure.
A Quick Guide to Rubber Types in Extrusion
Silicone rubber stands out for its exceptional resistance to temperature, UV, ozone, and weathering. However, silicone has relatively lower mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and abrasion resistance, compared to other rubbers. The varied applications of rubber extrusions mean one type of rubber is not always the best. Here’s a look at how different types of rubber stack up.
EPDM Rubber: Known for its hardiness, EPDM offers excellent resistance to UV and ozone, similar to silicone, but it can only handle temperatures up to around 135°C. It's widely used in outdoor applications like window and door seals.
Neoprene Rubber: Neoprene has higher mechanical strength than silicone and is resistant to water, chemicals, and oils. It’s often used in industrial settings and for applications requiring durability and flame resistanceapplications.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR): Nitrile is favoured for its excellent oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for automotive applications. However, it lacks silicone's temperature and weather resistance.
Viton: This fluorine-containing rubber excels in chemical resistance, particularly to concentrated acids and alkalis. It surpasses silicone in durability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for more aggressive environments
Product | Silicone Rubber | Natural Rubber | EPDM Rubber | Neoprene Rubber | Nitrile Rubber | Viton Rubber |
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
Medical Tubing | ✔ | |||||
Electrical Insulation | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
✔ | ✔ | |||||
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
Hoses | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
Food Processing Seals | ✔ | |||||
Weatherstripping | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
Conveyor Belts | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
Vibration Dampeners | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |
Expansion Joints | ✔ | ✔ |
Future Trends in Silicone Rubber Extrusions
Silicone rubber recycling has made significant advances in recent years. Traditionally, mechanical recycling of silicone was limited and often resulted in downgraded properties, restricting use to low-grade applications. However, new chemical recycling processes now allow used silicone products, such as caulk, sealants, and gaskets, to be broken down to their molecular building blocks and reprocessed into high-quality silicone, with no loss of performance. This “infinite” recycling loop can drastically reduce the sector’s environmental impact and reliance on virgin raw materials. In the UK, innovative products like Silicrumb, made from recycled silicone, demonstrate that recycled silicone can match the technical properties of virgin material and be used in extrusion and moulding applications. As these technologies scale, more silicone extrusions will be designed with recyclability and circularity in mind.
The properties of silicone rubber combined with ever-evolving developments in the extrusion process have paved the way for innovations in design and manufacturing. Here are three examples of cutting-edge creative endeavours made possible thanks to silicone rubber extrusion.
3D Printing with Silicone Rubber
Wacker Chemie AG developed a 3D printing technology called ACEO® that allows for the additive manufacturing of silicone rubber. This innovation combines traditional extrusion methods with advanced 3D printing techniques to create complex, custom silicone parts layer by layer. Apart from enabling the realistic reproduction of human organs and biocompatible silicone rubber components, applications range from medical devices and prosthetics to automotive components and wearable technology, offering enhanced precision and design flexibility.
Silicone Rubber for Medical Wearables
Companies like MC10 develop soft, stretchable electronics using silicone rubber as a key material. Its BioStampRC® sensor is a wearable device that adheres to the skin using silicone rubber, conforming to the body's contours and providing continuous health monitoring. This innovation is crucial for medical diagnostics, sports performance tracking, and remote patient monitoring, offering comfort and biocompatibility.
A 2018 study on using the BioStampRC® sensor for detecting respiration, cardiac, and limb movement signals during sleep found that it accurately captured respiration, ECG, and leg EMG signals during sleep, comparable to gold standard PSG, with 88% of participants willing to use it at home.
Advanced Silicone Rubber Seals for Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Innovative extruded silicone rubber seals are now being used in hydrogen fuel cell technology. For instance, the seals developed for hydrogen fuel cells in next-generation eco-friendly vehicles are made from specially formulated silicone rubber that can withstand the high pressures and temperatures of hydrogen fuel storage and conversion. These extruded seals ensure the containment and efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells, contributing to the advancement of clean energy technologies.
Find out more about rubber extrusion here and why it’s responsible for many innovations in hundreds of industries. Or take a look at our services in rubber extrusion, creating rubber profiles, rubber fabrications, mouldings, and many more methods for producing bespoke products.




news
Continue reading
Speak to One of Our Experts
Contact UsLEARN
INDUSTRIES
PRODUCTS
BRANDS
GET IN TOUCH


- © 2026 Nufox. All rights reserved |
- Terms & Conditions |
- Privacy Policy |
- Download ISO Certificate | Web Design MadeByShape